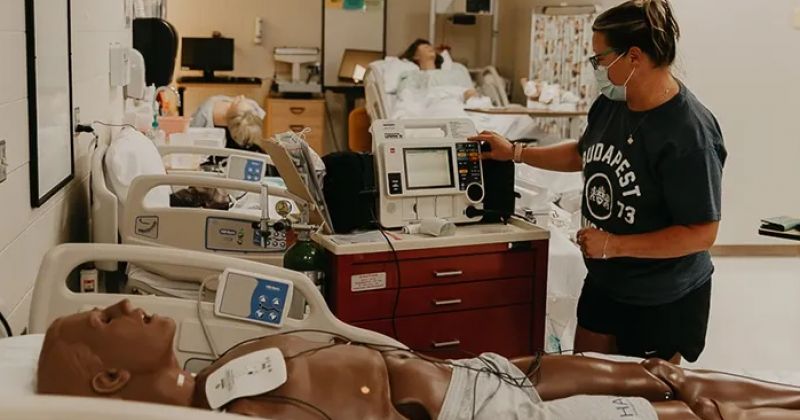
Informasi
Pandemi COVID-19 telah menciptakan kekurangan staf di seluruh rumah sakit Michigan, terutama di kalangan perawat. Rumah sakit pedesaan adalah yang paling terpukul karena mereka berjuang untuk memenuhi tingkat staf yang memadai bahkan sebelum pandemi. Mempertahankan rasio perawat-ke-pasien yang rendah adalah kunci untuk perawatan pasien yang lebih aman dan hasil yang lebih baik. Namun, sekolah keperawatan tidak dapat meluluskan perawat yang cukup untuk mengimbangi permintaan. Untuk mengatasi masalah ini, Alpena Community College (ACC) di timur laut Michigan menggunakan simulasi dalam program pendidikan keperawatannya untuk membantu melatih lebih banyak perawat dan memastikan mereka dapat memberikan perawatan yang lebih baik bagi pasien di...
Baca Selanjutnya
Informasi
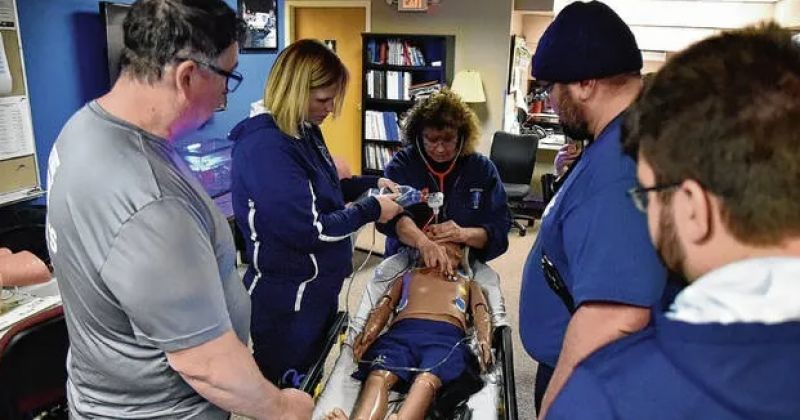
Sejak 2018, Indiana mengalami peningkatan panggilan ambulans tetapi penurunan pekerja EMS [1]. Hal ini menyebabkan waktu tunggu yang lebih lama untuk layanan ambulans, yang dapat berdampak negatif pada hasil, terutama selama keadaan darurat seperti stroke atau cedera traumatis. Jadi, EMS di negara bagian sering mengandalkan sukarelawan untuk mengisi posisi terbuka, meskipun kekurangan dana untuk melatih para pekerja ini. Namun, Laboratorium Simulasi Seluler Indiana membantu mengatasi kesenjangan pelatihan dengan memberikan pelatihan langsung berbasis simulasi kepada responden pertama di seluruh negara bagian, memastikan mereka siap untuk keadaan darurat kehidupan nyata dan bahwa pasien menerima perawatan berkualitas tinggi.
Baca Selanjutnya

Informasi
Efek dari kekurangan perawat selama pandemi Perawat memenuhi peran integral dalam mendukung dan memberikan layanan kesehatan yang berkualitas. Rumah sakit dengan staf perawat yang memadai mengalami penurunan kesalahan medis, morbiditas dan mortalitas pasien yang lebih rendah, dan kelelahan kerja yang jauh lebih sedikit daripada rumah sakit dengan rasio pasien-ke-perawat yang tinggi [1]. Namun, kekurangan perawat telah mempengaruhi AS sejak 2012, membutuhkan 1,2 juta perawat terdaftar (RN) baru pada tahun 2030 untuk mengatasi kekurangan tersebut[2]. Pandemi COVID-19 memperburuk kekurangan perawat yang ada; hingga satu dari lima petugas kesehatan telah meninggalkan pekerjaannya karena terlalu banyak bekerja, stres, dan trauma yang disebabkan oleh...
Baca Selanjutnya




